摘要
我们需要为不同的物体选择不同的材料,这需要设计方案管理决策。我们可以使用通用材料,并将某些主要参数归零来实现不同的效果。或者,我们可以使用一个抽象的材料类来封装个性化的行为。我更喜欢后一种方式。
正文
《Ray Tracing in One Weekend》阅读心得 – 9、Metal(金属材料)
如果我们期待不一样的物件应用不一样的原材料,则必须开展设计方案管理决策。我们可以应用具备很多主要参数的通用性原材料,而将不一样的原材料种类仅将在其中一些主要参数归零。这不是一个坏方式 。或是我们可以有一个抽象性的材料类来封裝个人行为。我是后一种方式 的粉絲。针对大家的程序流程,原材料必须做2件事:
- 造成透射放射线(或说它消化吸收了出射放射线)。
- 假如透射,讲出应将放射线衰减系数是多少。
这提议了抽象类:
9.1. An Abstract Class for Materials( 原材料抽象类)
#ifndef MATERIAL_H
#define MATERIAL_H
#include "rtweekend.h"
#include "hittable.h"
struct hit_record;
// abstract class
class material {
public:
virtual bool scatter(
const ray &r_in, const hit_record &rec, color &attenuation, ray &scattered
) const = 0;
};
#endif
material.h The material class
9.2. A Data Structure to Describe Ray-Object Intersections(叙述放射线目标交叉的算法设计)
hit_record是为了更好地防止应用一堆主要参数,因而我们可以在这其中添充需要的一切信息内容。 您能够改成应用主要参数。 这是一个品位难题。 hittables和material必须彼此之间掌握,因而论文参考文献有一定的回收再利用。 在C 中,您只必须警示c语言编译器该表针是一个类,下边的hittable类中的“类原材料”就这样做的:
/*该建筑结构纪录“撞点”处的信息内容:离光源起始点的间距t、撞点的座标空间向量p、撞触发的法向量normal.*/
struct hit_record {
point3 p;
vec3 normal;
// new variables
shared_ptr<material> mat_ptr;
double t;
bool front_face;
}
hittable.h Hit record with added material pointer
大家在这儿设定的是原材料将告知大家放射线怎样与表层相互影响。 hit_record仅仅将一堆主要参数添充到构造中的一种方式 ,因而我们可以将他们做为一组推送。 当光源碰撞表层(比如特殊的圆球)时,hit_record中的材料表针将被设定为偏向在我们逐渐时在main()中设定该圆球时需给出的材料表针。 当ray_color()方法获得hit_record时,它能够启用材料表针的友元函数来找到透射的光源(如果有)。
class sphere : public hittable {
public:
sphere() {}
sphere(point3 cen, double r, shared_ptr<material> m)
: center(cen), radius(r), mat_ptr(m) {};
virtual bool hit(
const ray& r, double t_min, double t_max, hit_record& rec) const override;
public:
point3 center;
double radius;
shared_ptr<material> mat_ptr;
};
bool sphere::hit(const ray& r, double t_min, double t_max, hit_record& rec) const {
...
rec.t = root;
rec.p = r.at(rec.t);
vec3 outward_normal = (rec.p - center) / radius;
rec.set_face_normal(r, outward_normal);
rec.mat_ptr = mat_ptr;
return true;
}
sphere.h Ray-sphere intersection with added material information
9.3. Modeling Light Scatter and Reflectance(仿真模拟光透射和透射率)
假如您认真阅读上边的编码,您会发觉一小撮捉弄的机遇。如果我们转化成的任意单位向量与反向空间向量彻底反过来,则二者之和将为零,这将造成 透射方向向量为零。这会在之后造成 欠佳状况(无穷和NaN),因而大家必须在传送标准以前先对其开展阻拦。
因此,大家将建立一个新的vector方式 —vec3::near_zero()假如矢量素材在全部层面上面十分贴近零,则回到true。
class vec3 {
...
bool near_zero() const {
// Return true if the vector is close to zero in all dimensions.
const auto s = 1e-8;
return (fabs(e[0]) < s) && (fabs(e[1]) < s) && (fabs(e[2]) < s);
}
...
};
vec3 The vec3::near_zero() method
// 兰伯特实体模型类
class lambertian : public material {
public:
lambertian(const color& a) : albedo(a) {}
virtual bool scatter(
const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, color& attenuation, ray& scattered
) const override {
auto scatter_direction = rec.normal random_unit_vector();
// Catch degenerate scatter direction
// 这时任意的空间向量类似为与normal法向空间向量反过来方位的空间向量
if (scatter_direction.near_zero())
scatter_direction = rec.normal;
scattered = ray(rec.p, scatter_direction);
attenuation = albedo;
return true;
}
public:
color albedo;
};
[material.h]The lambertian material class
9.4. Mirrored Light Reflection(镜面玻璃光的反射)
针对光洁的金属材料,放射线不容易被任意透射。重要数学课是:放射线怎样从金属材料镜反射面回家? 空间向量数学课是我们的朋友在这儿:
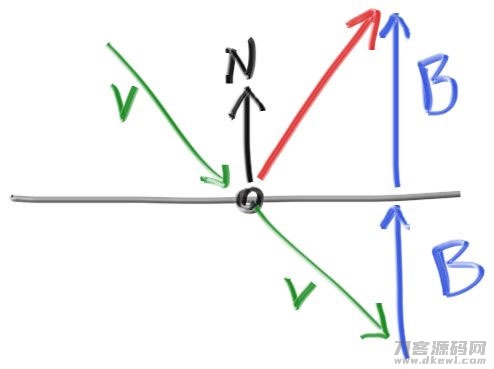
Figure 11: Ray reflection
鲜红色的反射面放射线方位为 v 6b。在大家的设计方案中n是单位向量,可是 v不一定。长短b 应当 v*n。由于v 点,大家将必须一个减号,造成:
// 反射面
// 法向是单位向量 因此点积結果便是空间向量v在n上投射的长短
vec3 reflect(const vec3 &v, const vec3 &n) {
return v - 2 * dot(v, n) * n;
}
[vec3.h]vec3 reflection function
金属复合材料仅仅应用该公式计算反射光线:
class metal : public material {
public:
metal(const color &a) : albedo(a) {}
bool scatter(const ray &r_in, const hit_record &rec, color &attenuation, ray &scattered) const override {
vec3 reflected = reflect(unit_vector(r_in.direction()), rec.normal);
scattered = ray(rec.p, reflected);
attenuation = albedo;
return (dot(scattered.direction(), rec.normal) > 0);
}
public:
color albedo;
};
我们要改动ray_color()涵数以应用此涵数:
color ray_color(const ray& r, const hittable& world, int depth) {
hit_record rec;
// If we've exceeded the ray bounce limit, no more light is gathered.
if (depth <= 0)
return color(0,0,0);
if (world.hit(r, 0.001, infinity, rec)) {
ray scattered;
color attenuation;
if (rec.mat_ptr->scatter(r, rec, attenuation, scattered))
return attenuation * ray_color(scattered, world, depth-1);
return color(0,0,0);
}
vec3 unit_direction = unit_vector(r.direction());
auto t = 0.5*(unit_direction.y() 1.0);
return (1.0-t)*color(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) t*color(0.5, 0.7, 1.0);
}
9.5. A Scene with Metal Spheres(金属材料球的情景)
在情景中加上一些金属材料球:
auto material_ground = make_shared<lambertian>(color(0.8, 0.8, 0.0));
auto material_center = make_shared<lambertian>(color(0.7, 0.3, 0.3));
auto material_left = make_shared<metal>(color(0.8, 0.8, 0.8));
auto material_right = make_shared<metal>(color(0.8, 0.6, 0.2));
world.add(make_shared<sphere>(point3( 0.0, -100.5, -1.0), 100.0, material_ground));
world.add(make_shared<sphere>(point3( 0.0, 0.0, -1.0), 0.5, material_center));
world.add(make_shared<sphere>(point3(-1.0, 0.0, -1.0), 0.5, material_left));
world.add(make_shared<sphere>(point3( 1.0, 0.0, -1.0), 0.5, material_right));
做好了
实际效果
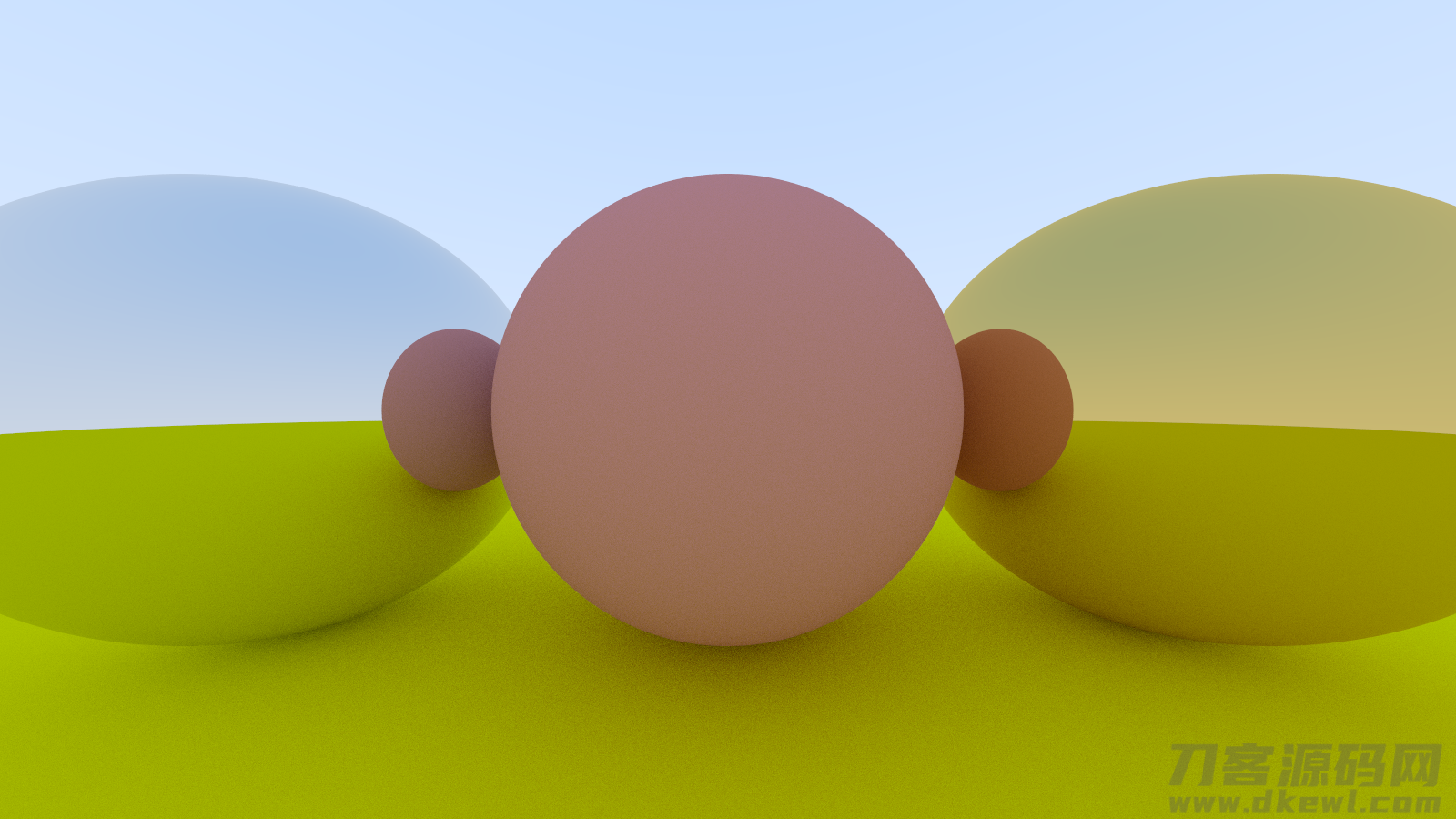
9.6. Fuzzy Reflection(模糊不清反射面)
大家还能够根据应用小圆球并为放射线挑选新的节点来随机化反射面方位:
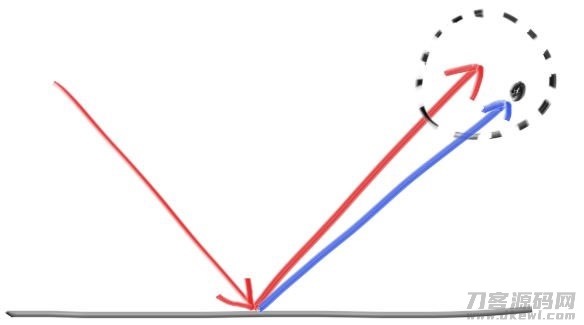 Figure 12: Generating fuzzed reflection rays
Figure 12: Generating fuzzed reflection rays
圆球越大,反射面将越来越越模糊不清。 这提议加上一个模糊不清度主要参数,该主要参数仅是圆球的半经(因而零是沒有振荡)。 要留意的是,针对大圆球或掠肉食性放射线,大家很有可能会透射到河面下列。 我们可以让表层消化吸收这些
// 金属材料类
class metal : public material {
public:
metal(const color &a, double f) : albedo(a), fuzz(f < 1 ? f : 1) {}
bool scatter(const ray &r_in, const hit_record &rec, color &attenuation, ray &scattered) const override {
vec3 reflected = reflect(unit_vector(r_in.direction()), rec.normal);
scattered = ray(rec.p, reflected fuzz * random_in_unit_sphere());
attenuation = albedo;
return (dot(scattered.direction(), rec.normal) > 0);
}
public:
color albedo;
double fuzz;
};
Listing 51: [material.h] Metal material fuzziness
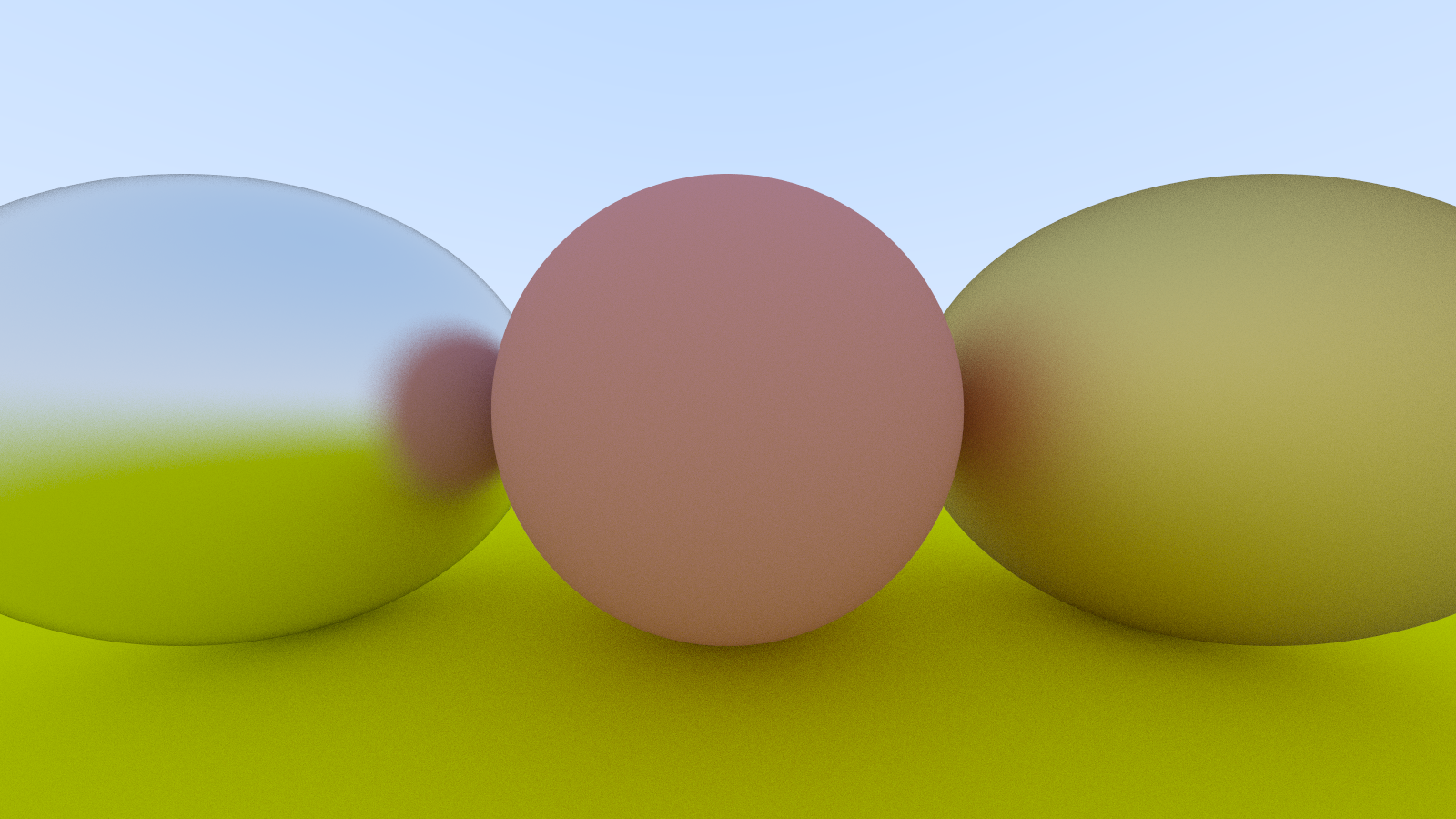
shared_ptr<metal> material_left = make_shared<metal>(color(0.8, 0.8, 0.8), 0.3);
shared_ptr<metal> material_right = make_shared<metal>(color(0.8, 0.6, 0.2), 1.0);
Listing 52: [main.cpp] Metal spheres with fuzziness
实际效果
这图确实太漂亮了QAQ
改动下随机函数,能看不一样的实际效果
// vec3 scatter_direction = rec.normal random_unit_vector();
vec3 scatter_direction = rec.normal random_in_unit_sphere();
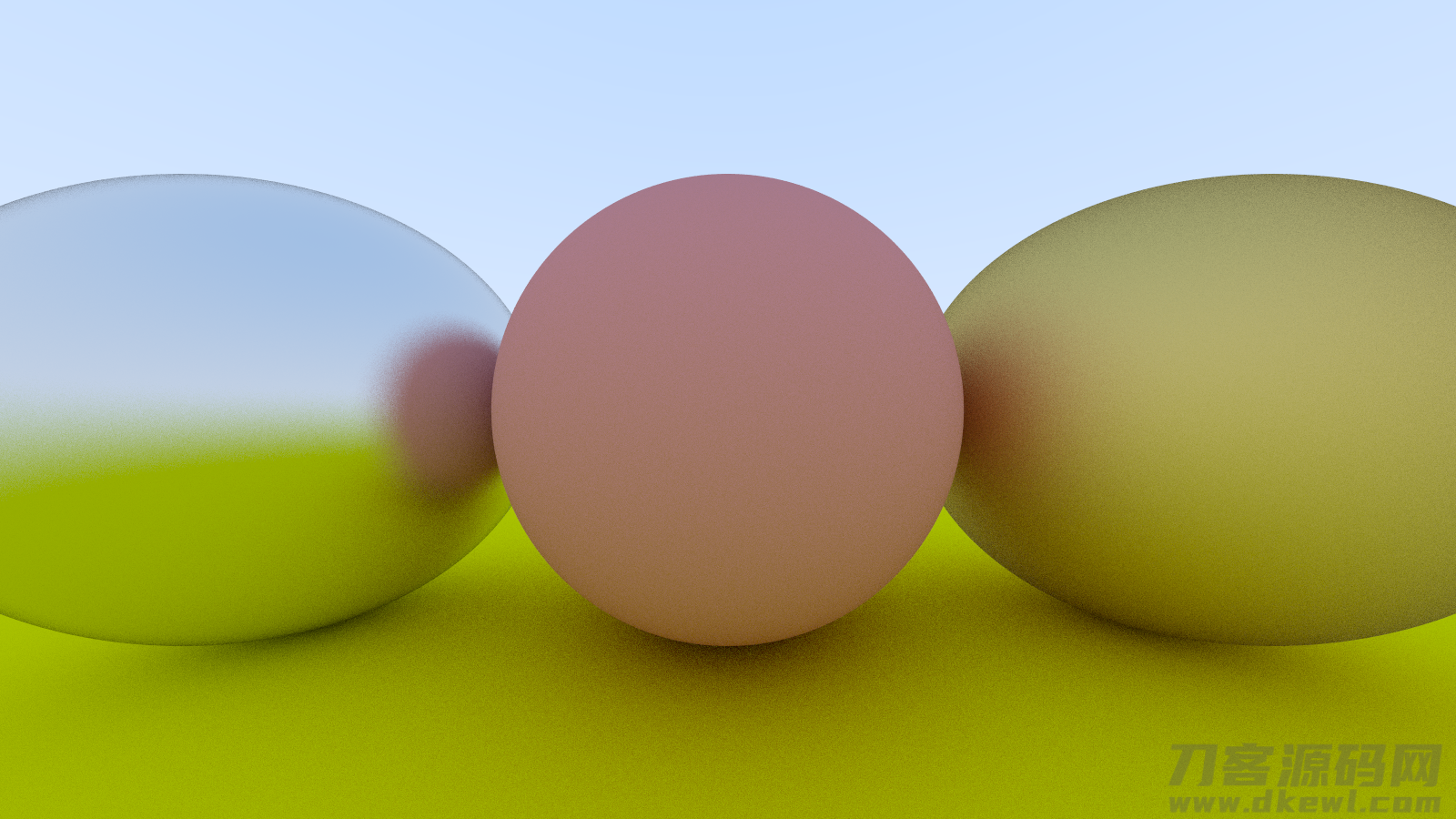
再改随机函数为半球型透射,再次跑,多看一下实际效果
// vec3 scatter_direction = rec.normal random_unit_vector();
// vec3 scatter_direction = rec.normal random_in_unit_sphere();
vec3 scatter_direction = rec.normal random_in_hemisphere(rec.normal);
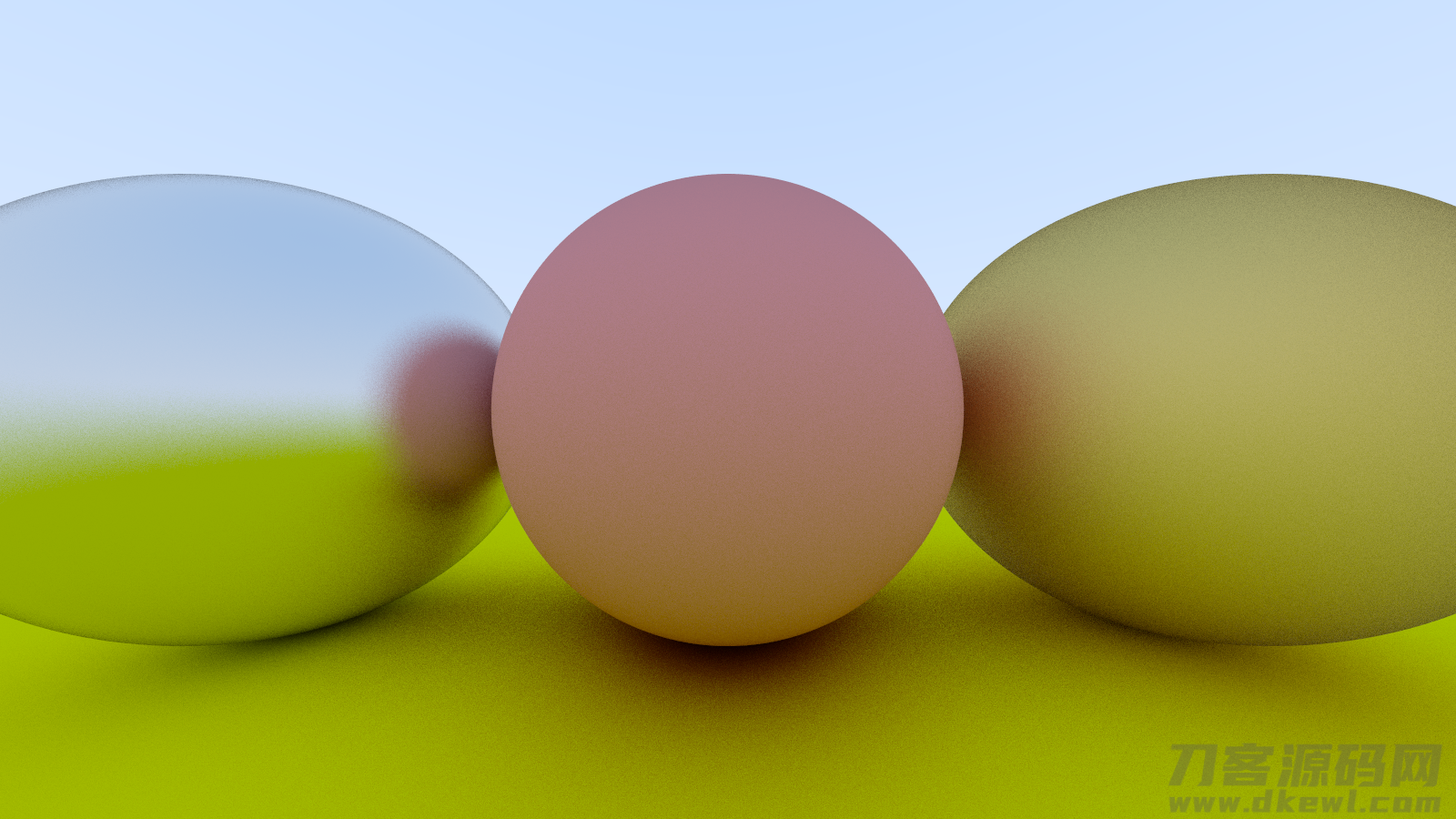
关注不迷路
扫码下方二维码,关注宇凡盒子公众号,免费获取最新技术内幕!






评论0